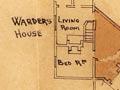
The Contagious Diseases Act 1869 allowed police to detain women they suspected of being prostitutes. If found to have venereal disease, the women were held for treatment. This plan of the Christchurch Lock Hospital, where those arrested under the act were held, shows that it was part of Addington Prison. The women were kept in conditions similar to those endured by other prisoners.
While sex workers were being blamed for spreading disease, men visiting them were neither detained nor examined. People who objected to the Contagious Diseases Act said that it 'made vice safe'. Rather than having to be chaste before marriage and faithful to his wife after, a man could visit prostitutes in the belief that he would not catch a venereal disease.
Te whakamahi i tēnei tūemi
Christchurch Regional Office, Archives New Zealand - Te Rua Mahara o te Kāwanatanga
Reference:
CH287, CP 343c, ICPS 1211-1872
Permission of Archives New Zealand Te Rua Mahara o te Kāwanatanga (Christchurch Regional Office) must be obtained before any re-use of this material.






Tāpiritia te tākupu hou